In the dynamic and ever-evolving landscape of business and technology, effective communication is key to the success of any project. One crucial document that plays a central role in this process is the Business Requirement Document (BRD). Whether you are a business owner, project manager, or a team member, understanding the significance of a well-crafted BRD is essential for steering your projects towards success.
What is a Business Requirement Document?
A Business Requirement Document, commonly known as a BRD, is a comprehensive document that outlines the objectives, scope, and functional requirements of a project. It serves as a bridge between business stakeholders and the development team, ensuring a clear understanding of what needs to be achieved and how it will be accomplished.
Key Components of a BRD:
- Project Overview:
- Define the purpose and goals of the project.
- Provide a high-level description of the business problem the project aims to solve.
- Scope and Objectives:
- Clearly outline the boundaries of the project.
- Define the specific objectives and deliverables expected from the project.
- Stakeholder Analysis:
- Identify and analyze key stakeholders.
- Specify their roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
- Functional Requirements:
- Detail the specific functionalities the system or product must possess.
- Provide use cases and scenarios to illustrate how users will interact with the system.
- Non-functional Requirements:
- Include performance, security, and usability requirements.
- Specify constraints that the project must adhere to.
- Assumptions and Constraints:
- Document any assumptions made during the planning phase.
- Outline constraints that may impact the project.
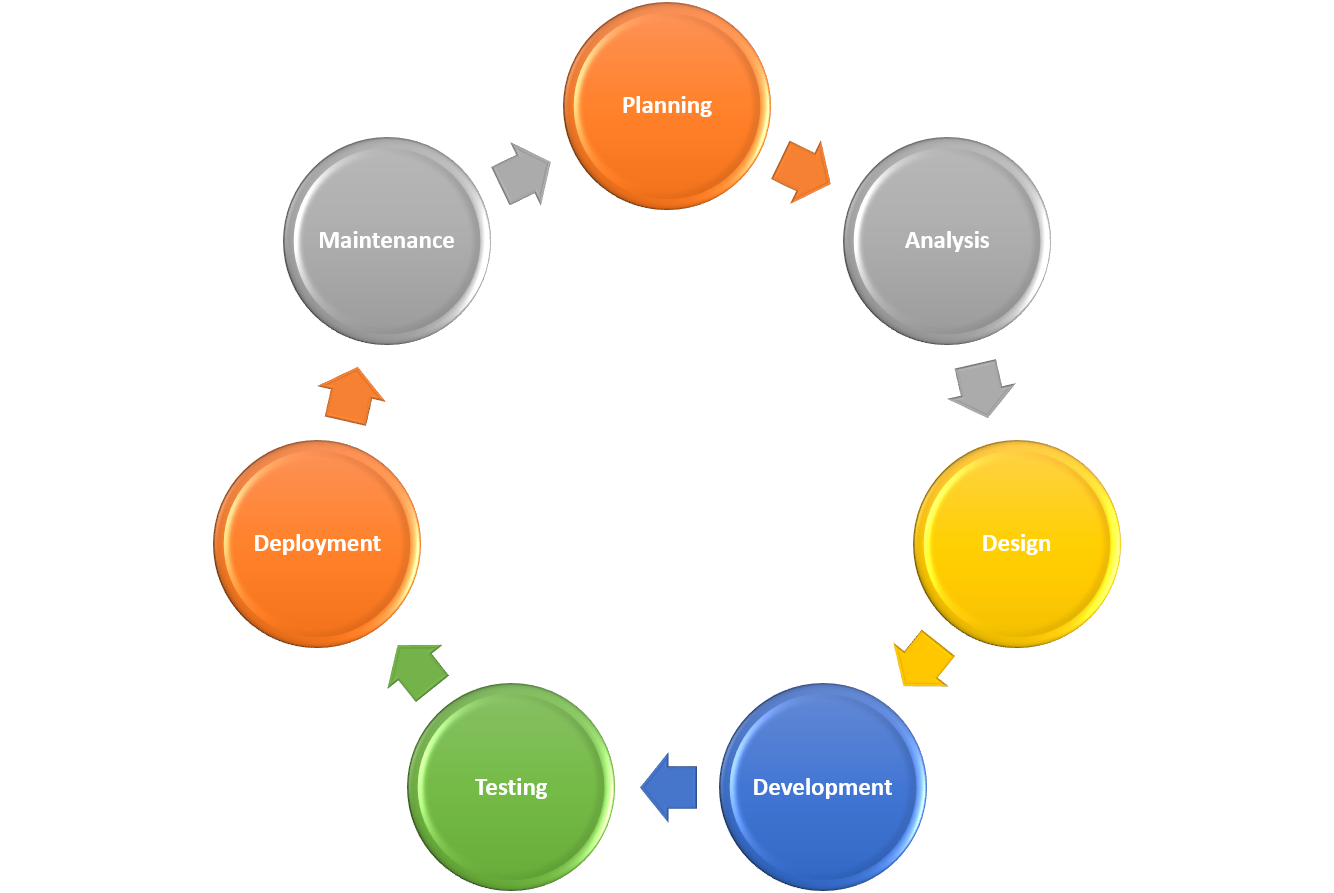
- Project Timeline and Milestones:
- Provide a high-level timeline for project completion.
- Define key milestones and deadlines.
- Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Outline the testing strategy and methodologies.
- Specify quality assurance processes to be followed.
- Approval and Sign-off:
- Clearly state the process for obtaining approvals.
- Include space for stakeholders to sign off on the document, indicating their agreement.

Importance of a Well-Defined BRD:
1. Alignment of Objectives:
> Ensures that all stakeholders are on the same page regarding project goals and objectives.
> Helps prevent misunderstandings that can lead to project delays or failures.
2. Clear Communication:
> Serves as a communication tool between business stakeholders and the development team.
> Reduces the risk of misinterpretation and ensures that everyone has a shared understanding.
3. Project Planning and Estimation:
> Provides a foundation for project planning and estimation.
> Enables accurate resource allocation and budgeting.
4. Risk Management:
> Identifies risk in the plan
> Facilitates the development of mitigation strategies.
5. Quality Assurance:
> Guides the development of test cases and ensures that the final product meets the specified requirements.
> Enhances the overall quality of the deliverables.
6. Change Management:
> Acts as a reference point for managing changes during the project lifecycle.
> Facilitates informed decision-making when alterations to the scope are proposed.
Conclusion:
In the realm of project management, a well-crafted Business Requirement Document is a cornerstone for success. It provides a roadmap that guides the project from conception to completion, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and aware of their roles and responsibilities. As businesses continue to navigate complex projects, the BRD remains an invaluable tool for fostering collaboration, reducing risks, and ultimately achieving project success.